Introduction to databases
Learning Objectives
A database is a structured set of data held in a computer. It provides ways to store, retrieve and organize information.
Why do we need them?
In the past few weeks, you stored and retrieved data using files. This is fine for simple data but it can quickly become an issue as your application becomes more complex and needs to store and manipulate more complicated data. For example, imagine you are asked to develop a booking system for a medium-sized hotel. You will need to store the list of rooms available for booking, and as you add more features, you will need to save users information, the reviews they post, the bookings each user makes and payment information. You can see that the data you need to handle can become very complicated, especially when you need to consider that data are not static, as they can be updated or deleted. To work more effectively with data, we can then use a database, which presents the following benefits:
- A database defines a structure for your data and the relationships between entities
- A database provides convenient and performant ways to safely store and retrieve data
- A database provides a mechanism to check the validity of your data
Different types of database
There are many different kinds of database and different implementations. Sometimes, a database type is a better fit to certain use case or certain problems. The most well-known database types include relational database, key/value database, graph database and document database (also known as NoSQL). For this class, we will focus specifically on relational database as they are the most widely used and supported. You can consult DB-Engines to see a ranking of the most used database, as you can see, there are a lot of them!
Youtube: What is a relational database?
Introduction to PostgreSQL
Learning Objectives
“PostgreSQL is a powerful, open source object-relational database system that uses and extends the SQL language combined with many features that safely store and scale the most complicated data workloads. The origins of PostgreSQL date back to 1986 as part of the POSTGRES project at the University of California at Berkeley and has more than 30 years of active development on the core platform.” (source: postgresql.org)
What is SQL?
- Pronounced S-Q-L or sequel
- Stands for Structured Query Language
- SQL is the standard language used to communicate with relational database
- SQL statements are used to query, create, update, delete records in a database as well as many other tasks
- SQL statements are executed by a RDBMS.
What is an RDBMS?
- Stands for Relational Database Management System
- It is a program that processes SQL statements to manage a relational database
- PostgreSQL is an RDBMS.
What characterizes a relational database?
As mentioned previously, a relational database is a specific type of database. Data is stored in tables (relations) of rows (tuples) and columns (attributes) as per the example below:
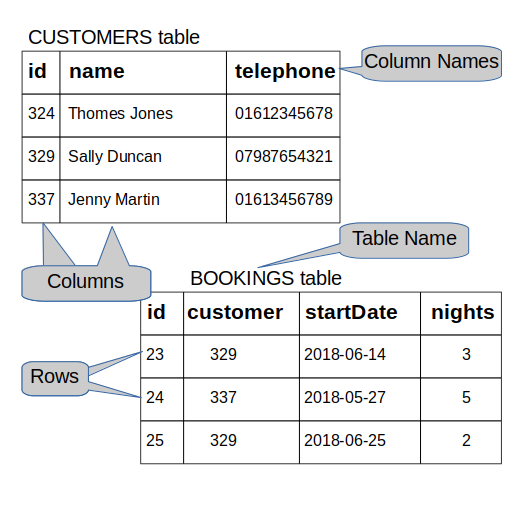
Youtube: Notes and exercises
Communicating with the database using SQL
Learning Objectives
👩🏽✈️👨🏾✈️Code along with video mentors
The PSQL utility
We use SQL to perform actions on the database and initially we can use a terminal-like utility to do this. The utility is named psql and is run using the command:
psql <dbname> <username>
The command prompt from psql is the database name currently connected:
my_hotel=>
In psql, you can use the command help to show the help menu. Within the command prompt, you can enter SQL statements and run them against PostgreSQL. To quit psql, enter the command \q.
Download the following file to a directory on your computer. This file creates the sample data you can use for the following sections. To do this, click the file to open it in a github formatted page, then right click the Raw button in the bar just above the code and select Save As (or Save Link As or similar) to save it:
Once you have the file downloaded to a known directory, execute the file build-hotel.sql from psql as shown below (replace /your/sql/path/ with the path to the download directory used above):
\include /your/sql/path/build-hotel.sql
Check that you have built all the required tables:
\dt
You should see a listing of your tables as follows (with your own username as owner):
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+---------------+-------+-------
public | customers | table | keith
public | invoices | table | keith
public | reservations | table | keith
public | room_types | table | keith
public | rooms | table | keith
(5 rows)
Here is the table diagram of the hotel database:
The SELECT Statement
We are first going to look at retrieving data from the database so we can examine it and later, use it in our applications.
To get data out of a table you use the SELECT statement (or command):
SELECT ... FROM ...;
For example:
SELECT name, phone, country FROM customers;
SQL commands entered in the psql command line tool are terminated with a semicolon (;). The SQL command can extend across several lines, but each keyword, name or value cannot be split over more than one line. For example:
SELECT name,
phone,
country
FROM
customers;
is the same as the previous example.
You can use SELECT * FROM ... to return all the columns of the table. For example:
SELECT * FROM rooms;
This is also a useful command to see what columns exist in a table. You can also use the \d <table_name> psql command to describe the table.
Note that the use of UPPER/lower case is only to emphasise and differentiate the SQL keywords (upper case) from the other names (lower case) e.g. column and table names. SQL keywords are not case-sensitive.
Scrolling the Results
When you issue a SELECT that returns a lot of data psql displays it one screenful at a time. To get the next screenful just press the Space key. You can also use the Up and Down arrow keys for line-by-line control and you can go back one screen with the ‘B’ key.
When you have finished reading the output use the ‘Q’ key to quit the display manager.
Space Next screenful
'B' Previous screenful
Down Arrow Next line
Up Arrow Previous line
'Q' Quit back to prompt
🕹️Test Your Skills
Some Useful psql Commands
The psql commands are not SQL and are specific to PostgreSQL (although most other RDBMS’s have commands to perform similar jobs). These commands let you display information, execute system commands, etc. Use \? to display a summary of all the psql commands.
Display a list of available tables in the database:
\dt
Display the definition of a table:
\d <table name>
Display help for SQL commands:
\h [command]
Display a summary of the psql (backslash) commands:
\?
Exit (quit) from psql:
\q
Note that psql commands ARE case sensitive, unlike SQL commands.
🕹️Test Your Skills
- Display the definition of the
customerstable - Display the help for the SELECT command (Note: we will not be covering ALL of this syntax!)
- Read the psql command help and find out what \dS does then try it
Displaying More Than Just Columns
You can use expressions in SQL:
SELECT room_no, rate * 0.85 FROM rooms;
+---------+-------------+
| room_no | rate * 0.85 |
+---------+-------------+
| 101 | 72.2500 |
| 102 | 72.2500 |
| 103 | 72.2500 |
...
Use a column alias to give the expression a meaningful name:
SELECT room_no,
rate * 0.85 AS discounted_rate
FROM rooms;
+---------+-----------------+
| room_no | discounted_rate |
+---------+-----------------+
| 101 | 72.2500 |
| 102 | 72.2500 |
| 103 | 72.2500 |
Here, the query uses the alias as the column heading. Aliases can also be used in other contexts - more on this later…
Expressions in SQL
As with Javascript you can use a variety of ‘operators’ to define expressions in SQL.
Arithmetic:
* Multiply
/ Divide
+ Add
- Subtract
% Modulo (remainder)
(...) Parentheses (to override precedence)
String:
|| Concatenation
For example, to display the weekly rate for a room (with 10% weekly discount):
SELECT room_no, room_type, rate * 7 * 0.90 from rooms;
You can change the column heading using a column alias:
SELECT room_no, room_type, rate * 7 * 0.90 as weekly_rate from rooms;
Use string concatenation to glue character data together:
SELECT 'Customer name = ' || name FROM customers;
Choosing the Rows
You can choose which rows to display by specifying some condition that must be matched:
SELECT id, name, phone, email, country
FROM customers
WHERE country = 'France';
id | name | phone | email | country
-----+--------------------+------------------+-----------------------------+---------
9 | Laurence Lebihan | 91.24.4555 | laurence.lebihan@xmzx.net | France
12 | Carine Schmitt | 40.32.2555 | carine.schmitt@dftu.net | France
15 | Janine Labrune | 40.67.8555 | janine.labrune@dlsh.net | France
25 | Mary Saveley | 78.32.5555 | mary.saveley@yppl.net | France
34 | Martine Rancé | 20.16.1555 | martine.rancé@xeqs.net | France
35 | Marie Bertrand | (1) 42.34.2555 | marie.bertrand@glut.net | France
49 | Frédérique Citeaux | 88.60.1555 | frédérique.citeaux@vekn.net | France
59 | Annette Roulet | 61.77.6555 | annette.roulet@lgha.net | France
62 | Daniel Da Silva | +33 1 46 62 7555 | daniel.da.silva@hijy.net | France
63 | Daniel Tonini | 30.59.8555 | daniel.tonini@mxvw.net | France
91 | Laurence Lebihan | 91.24.4555 | laurence.lebihan@xmzx.net | France
92 | Paul Henriot | 26.47.1555 | paul.henriot@uwua.net | France
106 | Dominique Perrier | (1) 47.55.6555 | dominique.perrier@bdim.net | France
(13 rows)
You can use comparison operators =, <, >, <=, >=, != (or <>)
Note: use only one = (equals) symbol to test for equality
When comparing numbers no punctuation is needed around the value, for example, WHERE rate > 100.
When comparing character data or dates you must enclose the values in single quotes (apostrophes), for example, WHERE name = 'Mary Saveley'.
Only the rows that match the comparison test (called a predicate) are returned by the query. The predicate can use columns not returned by the query,
Combining Tests in a Predicate
Use AND and OR to combine tests:
SELECT * FROM reservations
WHERE room_no >= 200
AND room_no < 300
AND checkin_date >= '2018-01-01';
This lists reservations for rooms on the second floor (rooms 200 - 299) since the start of 2018. Note the format of the date value - this conforms to the ISO 8601 standard and should be used in preference to any other format to avoid ambiguity.
Another example - to find cheap or Premier rooms on floors 1 and 2 - we might try this to start with:
SELECT * FROM rooms
WHERE room_type = 'PREMIER'
OR rate < 100.00
AND room_no < 300;
This isn’t quite right - it returns rooms on the 3rd and 4th floors. Why?
Overriding Evaluation Order
Just like any programming language, SQL has an evaluation order (precedence). For example, multiply and divide take precedence over add and subtract, so that:
SELECT rate + 20 * 0.85 from rooms;
is not the same as:
SELECT (rate + 20) * 0.85 from rooms;
We can override the normal precedence by using parentheses (...) around parts of the expression, just as in JavaScript.
With compound predicates AND takes precedence over OR, so that to make the query give the intended results we need to use:
SELECT * FROM rooms
WHERE (room_type = 'PREMIER'
OR rate < 100.00)
AND room_no < 300;
More Predicate Types
The BETWEEN operator has the form a BETWEEN b AND c : checks that a is in the range b - c inclusive. For example:
SELECT ... WHERE price BETWEEN 100 AND 250 ...
Note that the AND in this case is not combining multiple predicates, it’s part of the BETWEEN operator.
The IN operator, a IN (b, c, d, ...) checks if the value of a is equal to any of b, c, d, etc… For example:
SELECT ... WHERE room_no IN (201, 202, 204, 206) ...
Both the BETWEEN and the IN operators can be inverted using:
... a NOT BETWEEN b AND c ...
... a NOT IN (b, c, d, ...)
The LIKE operator tests for a match against a wildcard string as a LIKE b where a is being tested and b is the wildcard string. The wildcard string contains text to be matched along with wildcard symbols ‘%’ and ‘_’.
%(percent) matches any number of any characters_(underscore) matches exactly one of any character
For example:
name LIKE 'A%' matches names starting with ‘A’
name LIKE '_a%' matches names that have ‘a’ as the 2nd character (note the initial underscore ‘_’)
name LIKE '%ow%' matches names containing the sequence ‘ow’ anywhere in the name
LIKE can be inverted using a NOT LIKE b
If you need to match for a string that includes one of the wildard characters you can use the ’escape’ character, which defaults to ‘\’ (backslash). For example:
str LIKE '% discount = 5\% %' matches any value in str that contains ‘discount = 5%’
LIKE is case sensitive in many SQL implementations so to make a case insensitive match you should either convert the tested value to either all upper or all lower case, for example:
lower(name) LIKE '%b%' matches any name that contains the letters B or b
Note: PostgreSQL also has the non-standard operator ILIKE that can perform a case-insensitive comparison - but avoid this to make code more portable.
🕹️Test Your Skills
- Which customers are from Norway?
- Which rooms can accommodate more than two people?
- Which invoices are dated after one month ago?
- How would last month’s invoices change if we gave a discount of 15%
- List all customers whose second name starts with ‘M’ (hint: there’s a space before the second name)
Using SQL Functions
You can use the built-in functions of SQL just as you can in JavaScript, but note that they are different (this is true of most programming languages) but there are also differences between SQL implementations.
You use functions to change values, usually of columns, wherever you can use a column, for example, in the selected list of values:
SELECT name, length(name) AS namelen, upper(email)
FROM customers;
This query also uses a column alias (namelen) to provide a meaningful column heading.
Functions are available that operate on all different datatypes.
Country names are mixed case so to make sure we always match regardless of the stored case we can use the lower function to find all customers from Manchester, UK:
SELECT * FROM customers
WHERE lower(country) = 'uk'
AND city = 'Manchester';
Assuming room rates include VAT at 20%, list room rates after VAT increases to 23.5% (from 20%), but round to the nearest pound:
SELECT room_no, room_type, rate AS old_rate,
round(rate * 100/120 * 123.5/100) AS new_rate
FROM rooms;
For further information on SQL functions see the official PostgreSQL documentation at https://www.postgresql.org/docs/12/functions.html (for version 12 - for other versions change 12 to the required version)
Date and Time in SQL
In SQL dates and times are held in an internal format but are represented externally (when entering values and displaying them) as strings;
- Text date format: ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ e.g. ‘2018-07-21’ = 21 July 2018
- Time format: ‘HH:mm:SS.ddd’ e.g. ‘14:32’
- Date/Time format: ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:SS.ddd’ e.g. ‘2018-07-21 15:26:04’
You can perform arithmetic on dates and times, for example:
SELECT cust_id, room_no, checkin_date,
checkout_date - checkin_date AS nights
FROM reservations
WHERE checkout_date = current_date + 1;
This query performs subtraction of one date from another (checkout_date - checkin_date) to calculate the number of nights the customer has stayed. It also performs addition (current_date + 1) to get tomorrow’s date so that it lists all reservations that will be checking out tomorrow.
Note: current_date is a postgres function that returns the current date.
Also note that there are many ways to get the same result - you may explore those for yourself.
You can also represent time intervals but the representations can be complicated and we shall not cover them here.
🕹️Test Your Skills
- Write a query to check that all booking dates are before their checkin dates
- We plan to offer a discount of 10% on all Premier and Premier Plus rooms next month. How much would we gain on each room if occupancy rose by 5 nights over the month.
- List all reservations for this month and the number of nights booked.
Eliminating Duplicates
“Which nationalities visit our hotel?”:
SELECT country FROM customers;
But how many values do you see returned for each country? If two customers come from a particular country that country will appear twice in the output. If more than two come from the same country then… But we only need to know the different countries.
To see each country only once, use the keyword DISTINCT, as follows:
SELECT DISTINCT country FROM customers;
The keyword DISTINCT must appear immediately after the keyword SELECT. If more than one column is selected then DISTINCT applies to the combined values of those columns.
Ordering the Returned Rows
If you want to see the data in a specific order, e.g. “List all customers alphabetically by name within each country”:
SELECT id, name, phone, email, country
FROM customers
ORDER BY country, name;
You can can add ASC (ascending, the default) or DESC (descending) after each column name in the ORDER BY clause to control the direction of sorting.
For example:
SELECT id, name, country, city
FROM customers
ORDER BY country DESC, city;
This will sort the data into descending alphabetic order of country then ascending order of city name within each country. The output will look something like this:
id | name | country | city
-----+-------------------------+--------------+-------------------
28 | Kelvin Leong | USA | Allentown
96 | Juri Yoshido | USA | Boston
132 | Valarie Franco | USA | Boston
100 | Allen Nelson | USA | Brickhaven
46 | Miguel Barajas | USA | Brickhaven
43 | Leslie Taylor | USA | Brickhaven
37 | Julie King | USA | Bridgewater
130 | Sue Taylor | USA | Brisbane
124 | Steve Thompson | USA | Burbank
29 | Juri Hashimoto | USA | Burlingame
36 | Jerry Tseng | USA | Cambridge
70 | Marta Hernandez | USA | Cambridge
112 | Dan Lewis | USA | Glendale
52 | Mary Young | USA | Glendale
13 | Jean King | USA | Las Vegas
89 | Brian Chandler | USA | Los Angeles
97 | Dorothy Young | USA | Nashua
83 | William Brown | USA | Newark
120 | Violeta Benitez | USA | New Bedford
79 | Wing Huang | USA | New Bedford
116 | Leslie Murphy | USA | New Haven
. . .
Note: you can order by columns that are not returned by the query.
Limiting the Number of Rows
You can reduce the number of rows returned by using the LIMIT clause at the end of the query:
SELECT id, name, phone, email, country
FROM customers
ORDER BY country, name
LIMIT 20;
The LIMIT clause is not normally used without the ORDER BY clause - without the ORDER BY clause rows can be returned in any arbitrary sequence.
Not all SQL implementations of SQL support LIMIT, some use TOP while Oracle uses ROWNUM.
🕹️Test Your Skills
- List the different room types and rates for all rooms avoiding duplicates.
- List customers’ names addresses and phone numbers in alphabetic order of names.
- List customers’ names, addresses, city and country in ascending order of country then reverse order of city within country.
- List the room number, type and the cost of staying 5 nights in each of the top 15 most expensive rooms.
Summary
In this lesson you have learned the use of databases and how relational databases are structured. You’ve also learned how to use basic single-table query commands in SQL and some of the special ‘backslash’ commands in psql. You have used the SELECT command to control the columns and values that are returned, the DISTINCT, ORDER BY and LIMIT clauses to control the order and numbers of rows returned and you’ve used the WHERE clause to choose the rows that you access. You have learned the INSERT command to add new data to the database
Next time we shall go on to more complex query constructs including joins, updates and deletes along with incorporating SQL into a node.js server.
Prep Working Software and Done
🤙🏽 FeedbackLearning Objectives
Introduction
Definition of "Done"
🎯 Goal: To get familiar with why teams completely “Done” software every sprint (30 minutes)
“Is it done done?”
Salesperson: Have you finished that feature you’re working on?
Developer: Yes! It’s done. I just finished 10 minutes ago.
Salesperson: Great - I have a Spanish customer who really needs it.
Developer: Oh! Well, they can’t see it yet because we haven’t updated the on-screen instructions. And our product owner hasn’t yet agreed that it meets the acceptance tests. And the UI text hasn’t yet been translated into Spanish. And it’s not even integrated into the development branch let alone the production branch.
Salesperson: So, when you said it was done, what did you mean exactly? When will you be “done done”?
This conversation shows why every software team needs to agree on exactly what they mean by “done” for their software. Whenever more than one person works on a single project, the team members must have a common understanding of what “done” means for them.
A simple definition of “done” may look something like this:
Our backlog items are “done” when:
- It passes all our unit tests
- It passes the acceptance criteria for the User Story
- Code follows our agreed style guide
- Code is reviewed by at least one other person
- Any relevant documentation is updated
- Code is delivered to the git development branch
- The product owner accepts it
Note that each team will have their own definition of “done” that works for them using the particular processes and quality methods they have agreed upon. Have they agreed to minimize any web graphics? Have they agreed to ensure their code works on certain web browsers? If so, these agreements will be reflected in their definition of “done”.
Also, teams often have different rules in their definition of “done” that apply to different types of backlog item. For example, a backlog item that affects UI components will perhaps include “changed components tested for blind users”, but a backlog item on server-side changes will need different rules.
As teams change their quality processes over time, they may well improve and update their definition of “done” to include further quality statements on usability, documentation, performance, metrics, and many other aspects of delivering high-quality software to production.
Acceptance Criteria vs Definition of “Done”
You’ve met Acceptance Criteria before. They are a list of tests that help developers know they are delivering the value of a User Story that the Product Owner expects. There is sometimes confusion between acceptance criteria and the definition of “done”.
The difference is that acceptance criteria are specific tests for a single backlog item to help the Product Owner and developers understand when that single backlog item delivers the expected value; whereas the definition of “done” applies to all backlog items that a team delivers and helps everyone on the team know explicitly what quality of working software is being delivered.
For example, if you have a user story to deliver a log-in function, the Product Owner might specify the following acceptance criteria:
- users go to the home screen when the password is correct
- error message displayed when user-id and password do not match
- registered users can reset their password via email
However, a definition of “done” might contain (amongst others) rules like these:
- All web pages can be navigated without using a mouse
- All web pages tested in both dark and light modes
- All web pages follow our standard styling
- …
In other words, you can use a combination of acceptance criteria and a definition of “done” to help you and your team ensure that you are always delivering high-quality, working software.
Further Reading
For further information, read this article.
Understand the roles
🎯 Goal: To understand the roles and the work they do you will need the knowledge in the class (30 minutes)
Different types of roles will impact a team delivering valuable “working software”. Below is a list of roles with different characteristics. Research about them using any tool you would like.
You will use these roles in your exercises in class, so make sure you understand their personalities.
- Lazy software developer
- “Hacker” software developer
- Bean-counter project manager
- Salesperson
- Proxy customer who is not the end user
- Customer’s lawyer, who wants to verify the progress
- Product Owner trying to maximise “value”.